SANs That Support Block Storage
SANs That Support Block Storage
What is a block? What is its meaning in structured programming? And what are the features of a SAN that supports block storage? Let’s find out. Continue reading for more information. This article will explain the basic semantics of the block and its characteristics. Then, we will explore the various types of SANs that support block storage. To learn more, read on. The following sections will introduce you to the concept of blocks.
The basic semantics of block
The basic semantics of the Block is the ability to group elements together in a page. A block can act like a div. The semantics of the block can make the code more readable for programmers, but the advantages of the block are not clear. Hopefully, this article has helped you understand the basic semantics of the block. Here is a simple example of a block. Described below are three examples of basic semantics of block.
The block allows the programmer to group many statements into one statement. This allows the programmer to specify the scope of the objects declared within. The outer blocks can’t be masked by objects with the same name. Blocks delimitation is done with parentheses, keywords, and curly braces. The use of parentheses isn’t required for all languages. This article will focus on the basic semantics of block in C.
The use of transitions between blocks and text is another common problem. While the concrete syntax of a general-purpose programming language is important for nascent developers, learning block programs in isolation may be a mistake. Instead, block-to-text translation tools can improve students’ ability to learn traditional languages. Until now, no empirical research has examined how students learn to transition from blocks to text. In the future, the semantics of blocks will be central to learning traditional languages.
Meaning of block in structured programming
A block is a unit of code. It consists of a sequence of statements, which are called statements, and it is used to define the scope of variables and objects. Unlike a function, which is defined within a single statement, a block can be nested within another, which is known as block structure. Many languages use the term block to describe a specific type of code. The following are examples of languages that use blocks:
Each block represents a different scope. Using this technique will help you write code that is clean, easy to read, and maintainable.
In computer programming, a block is a group of statements and data definitions that are delimited by braces. The braces that surround a block act as brackets and all data enclosed within them are treated as a single statement. It also defines a local scope and defines whether a data object is local to a specific block. Similarly, a block does not redefine the data object’s identifier, which makes it useful for nested applications.
When using Python, is a section of code that has a specific purpose. Blocks are also important for ensuring the structure of a Python program. They can be any combination of statements and algorithms and are very useful for organizing complex software. So, if you are looking for a programmable block, be sure to read up on it!
Characteristics of blocks
Parametric pumping characteristics of blocks A, B, and C are studied. All three blocks have identical lengths and thicknesses, but different widths. Measurements are made of the pumping threshold using micro-Brillouin light scattering spectrum, spatial profiles, and dispersion relation. The profiles reveal the sensitivity of pumping thresholds to changes in the size and shape of the blocks. This study helps us understand the role of size in the pumping threshold and the nature of spin waves in the block.
Among the major geometrical properties of blocks, shape index, area, and water absorption are important for engineers. These properties enable structural engineers to compute their design calculations. Without these characteristics, they often have to rely on speculations and approximations, which can be problematic for structures. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain and use these physical properties of blocks for the design of structures. The use of these data is a prerequisite for efficient construction and maintenance of structures.
The characteristics of blocks have a profound effect on the city’s development. In fact, modern cities have evolved to recognize their characteristics through their street networks. For instance, Beijing City Lab defines a block as a piece of land surrounded by the main roads of the city, secondary roads, and branch roads. It gives 4594 city blocks to use as examples. The statistical data collected in the research are particularly helpful for building up an appropriate classification and focusing analysis.
A recent study shows that blocks can be a very important factor in shaping cities. These studies have shown that the distribution of blocks is a good reflection of the regional climate, which is the result of climatological variability. Moreover, these studies also show that blocking activity is more intense during the winter. And they also reveal the fact that the distribution of blocks is similar to that of VAPV and Z500*. Both models exhibit similar maxima along the southern hemisphere midlatitudes, including over the British Islands and Aleutians.
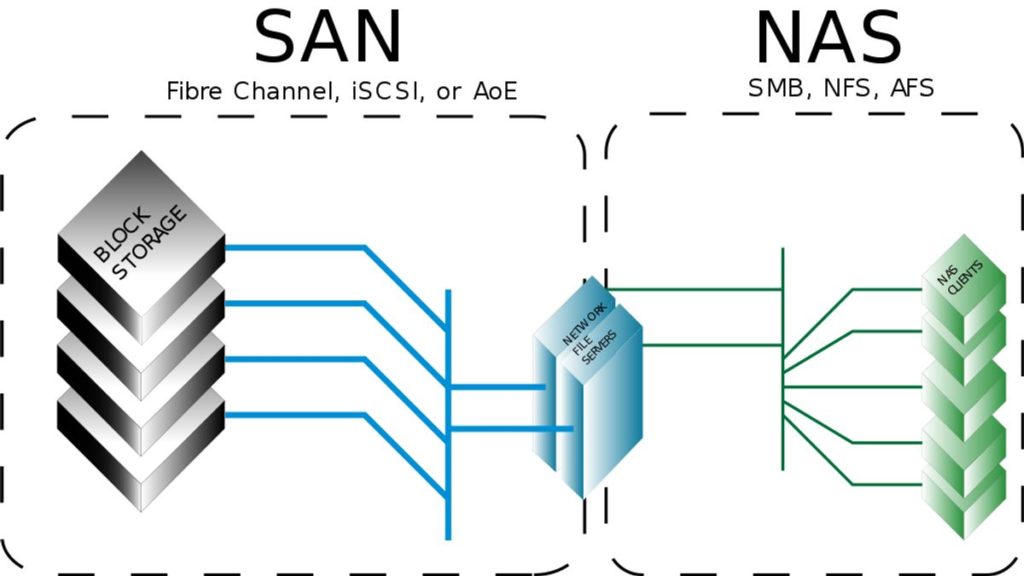
SANs that support block storage
This design allows centralized storage management and can improve storage security and application availability. The SAN also allows users to perform multiple backups of data and applications. For more information on SANs and their benefits, read on. This article will discuss some of the most common advantages of SANs that support block storage.
Traditional SANs support block storage but don’t offer data file abstraction. File systems run on dedicated LUNs to avoid interference between different systems. A shared LUN can cause data corruption if multiple systems share the same LUN. For planned data sharing between computers, shared-disk file systems are available. The SAN network devices move data from initiators to receivers.
SANs that support block storage typically use Fibre Channel (FC) technology. This protocol maps SCSI commands to FC technology. However, some systems use Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), which converges storage and IP protocols onto a single cable. Other less expensive SANs use iSCSI over Ethernet or InfiniBand. Regardless of the type of SAN technology used, there are different types available.
SANs that support block storage offer advantages that traditional NAS systems cannot provide. Block storage decouples data from user environments and adds a layer of abstraction. Data retrieval and capacity allocation are more complicated than in a NAS system. Moreover, the use of multiple data access paths speeds up data retrieval. These benefits may outweigh the increased complexity of a traditional SAN. So, before buying one, make sure you understand its benefits and drawbacks.
Construction of blocks
Blocks are also relatively cheaper than concrete or other construction materials. Precast construction is often cheaper, but is also inconvenient for urban construction. It requires third-party factories to make the blocks, which can be unreliable and expensive. Traditional construction is space-intensive and can be hazardous. Blocks are also unforgiving for weather, making them inconvenient for use in urban areas. And if you don’t have any access to a quarry, it can be difficult to transport large amounts of the material to the site.
Another method for building blocks is off-site construction. Off-site construction involves constructing the blocks at a factory, transporting them to the site, and assembling them to form the structure. As with any other construction method, this method has its advantages and disadvantages, and it is best to consult with a block supplier for the specific scenario. In most cases, however, off-site construction is the best option. Aside from reducing the construction time, this method also ensures better quality.
The production of concrete blocks involves four basic processes. Sand and gravel may also contain ultrasonic sensors to detect any trapped water. Concrete blocks are then cured under low or high pressure in a steam oven. They may be used to construct foundations, load-bearing walls, and retaining walls. For more information Please Visit This Site.




